Understanding the Essential Elements for Neurowellness
The adaptive and holistic approach developed and taught by Neurolead® is summarised as The Five Elements of Neurowellness®. Our approach to neurowellness aims to ensure that the diverse and unique needs of the brain, mind, body and spirit of each individual are addressed, promoting not only optimal, sustainable neuro-cognitive performance and health but also a meaningful quality of life that is rich in mental clarity, emotional balance, and overall purpose.
1: emotional neurowellness
Emotional wellness can be defined as the ability to recognise emotional reactions in the body and effectively manage the automatic responses to those emotions through self-awareness and self-regulation. Gaining the ability to emotionally self-regulate results in greater emotional control and balance, becoming better able to self-regulate the ‘fight-flight-freeze’ response during times of stress, challenge and change, resulting in increased resilience.
Hence the term emotional neurowellness, the resultant state from practiced self-awareness and emotional self-regulation of the autonomic nervous system.
2: psychological neurowellness
Being psychologically well encompasses the ability to live mindfully with self-awareness, to recognise, accept and change thoughts and emotions, in order to adapt behaviour, habits and choices.
As an individual learns to emotionally self-regulate, not only does emotional neurowellness improve, but so too does psychological neurowellness develop, and individuals can find themselves better able to ‘keep calm and carry on’, also more likely to achieve more ordered and enhanced cognitive function with an increased ability to ‘see more clearly’ or embrace the ‘bigger picture’ as a result.
3: physiological neurowellness
Not only is psychological wellbeing more likely to improve as emotional self-regulation increases, but so too will physiological neurowellness likely develop as the physical body experiences less stress and increased homeostasis or balance. However, this essential element for neurowellness can be further nurtured and supported by proactively embracing regular physical activity, optimising sleep[i] and ensuring that the physical environment is one that cultivates overall physical wellbeing.
4: Nutritional Neurowellness
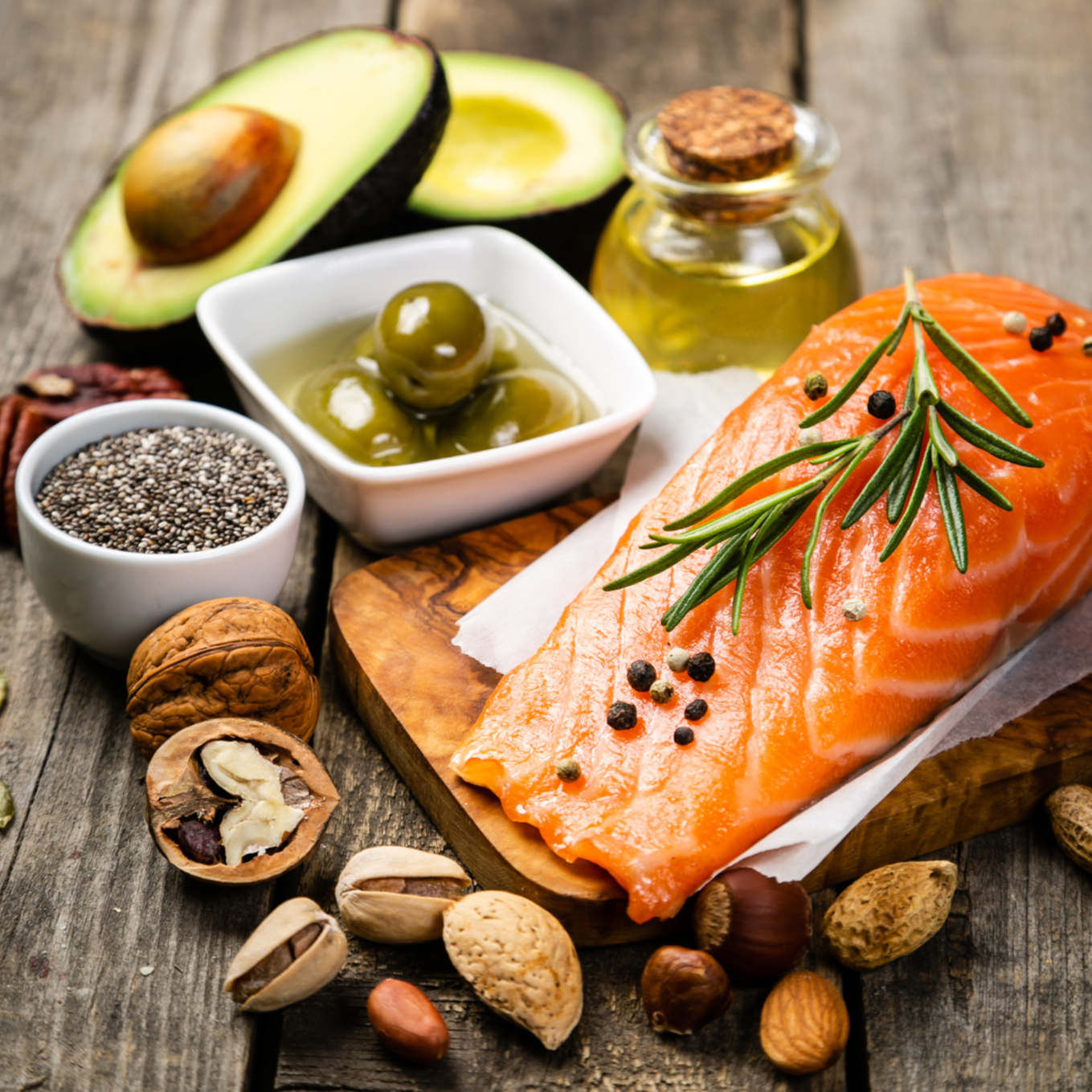
Nutritional neurowellness is a fundamental element for nurturing neuro-cognitive health and wellbeing as the nervous system, the brain in particular, requires specific nutrients to function optimally.
The brain is the fattiest organ in the body[ii] and is estimated to consume 25% of any energy consumed. A neuro-friendly diet requires high quality fibre, protein and healthy fat and will therefore be rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals necessary to support neuro health and cognitive function[iii].
Emerging research is also shedding light on the role of gut health in cognitive function, suggesting that the gut-brain axis is a crucial component in maintaining mental health[iv].
5: spiritual neurowellness
Spiritual wellbeing can be defined as a balanced connection to ourselves and the world around us, living with clear purpose and meaning, with evolving and developing awareness[v][vi]. Achieving holistic or overall wellbeing, including neurowellness, therefore necessitates incorporation of this aspect of wellness, integrating emotional, psychological, physical and spiritual practices that promote overall health and wellbeing.
In essence, spiritual neurowellness encourages authentic living, acknowledging individuals purpose and meaning with increasing existential awareness and development, exploring what it means to each of us to be alive at this time, enriching and enhancing our overall life experience as a result.
references:
[i] Ramar, K. et al. (2021). Sleep is essential to health. https://jcsm.aasm.org/doi/10.5664/jcsm.9476
[ii] Chang, C-Y., Ke, D-S. & Chen, J-Y. (2009). Essential fatty acids and the human brain. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20329590/
[iii] Gómez-Pinilla, F. (2008). Brain foods: The effects of nutrients on brain function. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 9(7), 568-578. doi:10.1038/nrn2421
[iv] Hameed, M. et al. (2024). Gut-Brain Axis: Investigating the Effects of Gut Health on Cognitive Functioning in Adults. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11315957
[v] Ryff, C.D. (2021) Spirituality and Well-being: Theory, Science and the Nature Connection. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8651234/
[vi] Rosenthal Centre for Wellness and Health Promotion, Harvard University Health Services, 2025. https://wellness.huhs.harvard.edu/your-wellbeing/wellbeing-framework/spiritual/